Mysql基础篇-约束
概念
约束是作用域表中字段的规则,用来限制数据
目的
保证数据库中数据的正确性,有效性,完整性
常见约束
| 约束 | 描述 | 关键字 |
|---|---|---|
| 非空约束 | 限制该字段不能为null | not null |
| 唯一约束 | 保证该字段的所有数据都是唯一不重复的 | unique |
| 主键约束 | 主键是一方数据的唯一标识,非空且唯一 | primary key |
| 默认约束 | 保存数据时,如果未指定字段的值,采用默认值 | default |
| 检查约束 | 保证字段值满足某一个条件 | check |
| 外键约束 | 让两表之间的数据产生链接,保证数据的一致性 | foreign key |
约束时作用于表中字段上的,可以在创建表,修改表的时候添加约束
– 这是GPT给出的答案,因为我一开始觉得主键没啥用
`PRIMARY KEY`` 在关系型数据库中有几个重要的作用:
- 唯一性约束:**
PRIMARY KEY** 用于确保表中的每行都有一个唯一的标识符。这意味着主键列中的值不能重复。这对于确保表中的每个条目都可以被唯一标识非常重要。- 索引:定义主键还会自动创建一个索引。这使得在主键列上执行的搜索和连接等操作更加高效。
- 外键引用:在其他表中,主键通常被用作外键的引用。这种引用确保了表与表之间的关联性。
因此,**
PRIMARY KEY** 在数据库设计中是非常重要的,它有助于确保数据的完整性、唯一性和高效性。
案例
| 字段名 | 字段含义 | 字段类型 | 约束条件 | 约束关键字 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ID唯一标识 | int | 主键,并且自动增长 | primary key , auto_increment |
| name | 姓名 | varchar(10) | 不为空,唯一 | not null ,unique |
| age | 年龄 | int | 大于零,小于等于120 | check |
| status | 状态 | char(1) | 默认为1(单位统一噢) | dafault |
| gender | 性别 | char(1) | 无 | / |
1 | create table people ( |
下面开始验证:
id 自增性
1
2-- 因为id字段是自增的所以数据库自己会维护,不需要插入, 且第一个数据id为1
insert into people (name, age, status, gender) VALUES ('Tom',19,'1','男'),('Tom2',25,'0','女');
name 非空性
1
2
3insert into people (name, age, status, gender) VALUES (null,19,'1','男'),('Tom3',25,'0','女');
-- Column 'name' cannot be null
-- 空时null 不是''
name 唯一性
1
2
3insert into people (name, age, status, gender) VALUES ('Tom',19,'1','男');
-- Duplicate entry 'Tom' for key 'people.name'
-- 表示唯一性,因为表中已经有一个Tom了
age 的check约束
1
2
3insert into people (name, age, status, gender) VALUES ('Tom5',130,'1','男');
-- 报错 Check constraint 'people_chk_1' is violated.
-- 130 这个数据不符合规定
检验默认值
1
2
3
4insert into people (name, age, status, gender) VALUES ('Tom7',29,null,'男');
-- 输出 status = null
insert into people (name, age,gender) VALUES ('Tom9',29,'男');
-- 输出 status = 1
- 注意: 当你这个插入语句不成立时,主键id还是会自增,因为他已经向数据库申请了一块空间,只是没显示……
外键约束 (主表从表关系有点绕)
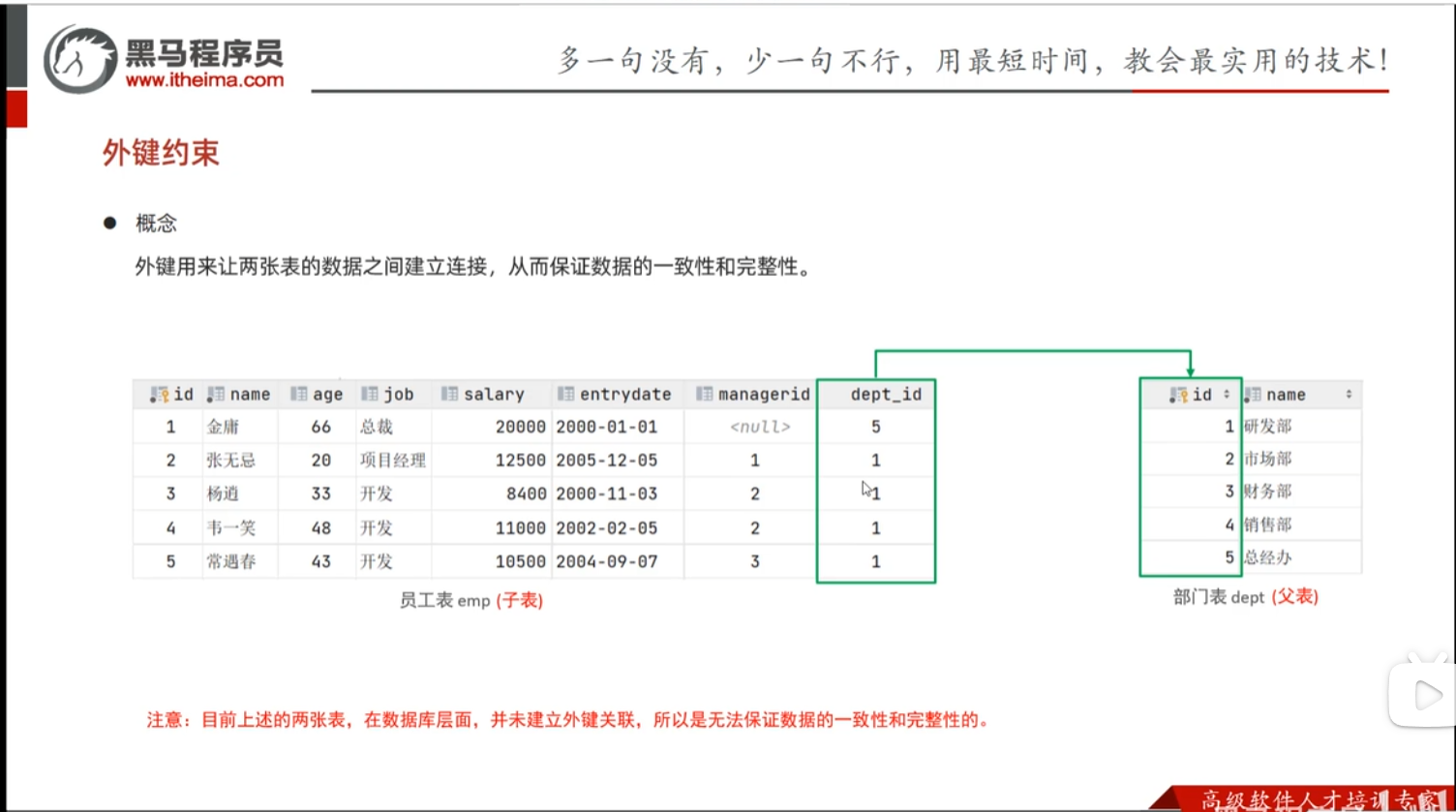
当删除父表中的数据,若该数据在子表中存在,则不允许删除该数据,保证了数据的一致性,安全性
MySQL的外键约束用来在两个表数据之间建立链接,其中一张表的一个字段被另一张表中对应的字段约束。也就是说,设置外键约束至少要有两种表,被约束的表叫做从表(子表),另一张叫做主表(父表),属于主从关系。
使数据更加完整,关联性更强。
其中主表中的关联字段叫做主键,外表中的关联字段叫做外键。
演示
1
2
3
4
5
6-- 从表
create table dept(
id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key ,
name varchar(50) not null comment '部门名称'
)comment '部门表';
insert into dept (id, name) values (1,'研发部'),(2,'市场部'),(3,'财务部'),(4,'销售部'),(5,'总经办') ;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15-- 主表
create table emp (
id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key ,
name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名',
age int comment '年龄',
job varchar(20) comment '职位',
salary int comment '薪资',
entrydate date comment '入职时间' ,
managerid int comment '直属领导ID' ,
dept_id int comment '部门ID'
)comment '员工表';
insert into emp (id, name, age, job, salary, entrydate, managerid, dept_id) values (...)- 在创建表时添加
create table 表名(
字段名 数据类型
…..
[constraint] [外键名称] + foreign key (外键字段名) + references 主表 (主表列名)
); – 约束名称可以省略+(从表字段)+主表(字段)
注意: 这边的字段都要加上括号,不加括号的话我也不知道,反正zhe’shi
参数说明:
CONSTRAINT :用于设置外键约束名称,可以省略FOREIGN KEY:外键设置,用于指定外键字段
REFERENCES:主表及主键设置,用于指定主表和主键
- 在修改表时添加
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段名)references 主表(主表列名);
1
2
3alter talbe emp add [ constraint fk_emp_dept_id ] foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);
-- 在这种情况下,“dept” 表的 “id” 列,被引用为 “emp” 表的外键 “dept_id”。因此,“dept” 表是父表,而 “emp” 表是子表。 dept_id
-- 外键字段名是从表(子表)中的字段,它引用了主表(父表)中的主键。- 删除外键
alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称;
1
alter table emp drop foreign key fk_emp_dept_id;
删除与更新行为(加最后)
行为 说明 no action 当父表删除/更新对应记录时,首先检查记录是否有对应外键,如果有不允许删除/更新(默认行为) restrict 当父表删除/更新对应记录时,首先检查记录是否有对应外键,如果有则不允许删除/更新(默认行为) cascade 当在父表中删除/更新对应记录时,首先应该检查是否有对应外键,如果有,则也删除/更新 set null 当在父表中删除对应记录时,检查子表有没有对应记录,有就设置null set default 父表有变更时,子表将外键设置为一个默认的值 (innodb不支持) - alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段) references 主表名 (主表字段名)on update cascade on delete cascade
- alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段) references 主表名 (主表字段名)on update set null on delete set null
